Anycast
Updated: 06/22/2024 by Computer Hope
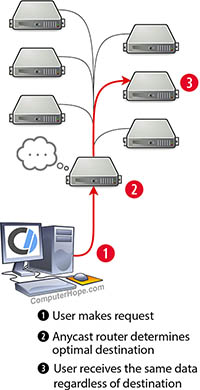
Anycast is a method for routing Internet traffic. In an anycast network, a router can dynamically determine the best destination for data packets. When a user requests data, traffic is routed to different servers depending on a set of determining factors. Regardless of which server is chosen as the destination, the user receives the same data.
Determining factors for destination choice
- Congestion — Like the speed of vehicles on a highway, network performance can be affected by the amount of traffic on any particular Internet route. Using anycast, servers with the least-congested route to the originating request can be chosen.
- Health — When a single server becomes very busy, it might be slow to respond to network requests. Servers that are less busy are considered "healthier," and may be chosen to receive new traffic.
- Geographical location — If a particular server is geographically close to the originating request, network traffic will travel a shorter physical distance, so that the request completes quickly. For instance, a user in Arizona loads a website faster if it's served from California rather than New York. This type of routing is also known as geocast.
- Cost — Sometimes, the cost associated with using some servers may be higher than others, in which case the lowest-cost server may be chosen to handle requests.
- Other — Custom factors can be defined by the service operator.
Anycast is one of the five top techniques for routing Internet traffic. The others are unicast, broadcast, multicast, and geocast.
BGP, CDN, DNS, Internet terms, Load balancing, Multicast, Network, Network terms, Routing, Traceroute
