CAPTCHA
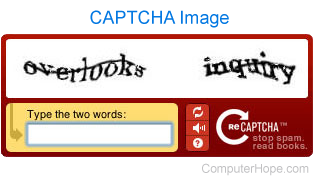
Short for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart, CAPTCHA is a protection that identifies humans from computers. Often, a CAPTCHA is an image of text, distorted so that humans can read it, but most automated computer vision system cannot. The picture shows a CAPTCHA.
In the picture, the visitor can visually identify the words "overlooks" and "inquiry" to validate they're human. Without this information being entered into the web page, a user would be unable to continue. Unfortunately, blind or hard of seeing visitors run into difficulties with CAPTCHAs because of the inability to read the letters shown in the image. To help these visitors access a page protected by a CAPTCHA, an audible CAPTCHA reads the letters aloud to the visitor.
Are CAPTCHA's case-sensitive?
No, a CAPTCHA is not case-sensitive, so if the same words mentioned earlier were entered in uppercase it would still work.
How is CAPTCHA pronounced?
CAPTCHA is an acronym that is sounded out. So, it would be pronounced as cap-cha.
Why does website ask if I'm a robot?
Software bots are written to perform common tasks such as a form submission to advertise on a website automatically. To protect against these bots, a website asks if you're a robot as a CAPTCHA to determine if you're a human or a robot. This protection is done by analyzing the mouse movements and looking for any other irregularities as the user checks the I'm not a robot check box.
History of CAPTCHA
The "T" in CAPTCHA stands for Turing test, a concept created by Alan Turing in 1950. The Turing test involves a human who observes two participants in a conversation and identifies which one is a human, and which one is artificial intelligence. A CAPTCHA takes this concept and, as the name implies, automates it.
The concept of a CAPTCHA was invented in 1997 by a team of people, including Manuel Blum, Nicholas J. Hopper, John Langford, Gili Raanan, Eran Reshef, Eilon Solan, and Luis von Ahn. They wrote about the idea and use of CAPTCHAs in a May 2003 publication titled "CAPTCHA: Using Hard AI (Artificial Intelligence) Problems for Security," and coined the "CAPTCHA" term that same year.
One of the earliest uses of CAPTCHA was the Gausebeck-Levchin test, a security measure created by Max Levchin and utilized by PayPal in 2001.
AI, Computer acronyms, Internet terms, Recaptcha, Reverse Turing test, Test
